
Hundreds of Thousands Have Already Played Cairn, but Another Game Tops 2026’s Scores
Indie climbing game Cairn has quickly become one of 2026’s biggest early hits, reaching more than 300,000 players shortly after
When it comes to buying a laptop, the CPU (Central Processing Unit) is one of the most critical components to consider.
This guide will help you understand laptop CPUs and how to choose the best one for your needs.
A laptop CPU (Central Processing Unit) is the brain of a laptop, responsible for executing instructions and managing various tasks together. Whether you’re opening an application, streaming a video, or playing a game, the CPU is working behind the scenes to do simple tasks and ensure smooth operation.

Laptop CPUs are designed to balance processing power, speed, energy efficiency, and heat generation. Unlike desktop CPUs, which prioritize raw power, laptop CPUs focus on delivering adequate performance while maintaining a compact and energy-efficient design.
Understanding core count, processing power, CPU cost, and architecture is vital when evaluating CPU performance:
The two dominant players in the laptop CPU market are Intel and AMD:
Ryzen processors also typically feature more cores and threads, making them excellent for multitasking and productivity. Plus, their desktop counterparts, right now, make for the best gaming PC. If you are interested in building AMD setups for gaming, we can surely help you out.

Both brands cater to a wide range of users from casual laptop users to professionals and gamers.
Laptop CPUs can be categorized into three performance tiers:
The choice between integrated and dedicated graphics depends on your usage:

For users focusing on general productivity, integrated graphics are usually sufficient. Gamers and creators should opt for dedicated GPUs paired with high-end CPUs.
Selecting the right CPU starts with understanding your usage patterns:

Balancing performance and power consumption is crucial for laptops:
To maximize battery life without sacrificing performance, consider CPUs designed for efficiency, like Intel’s EVO-certified processors or AMD’s Ryzen 6000 series processor.
When choosing a new laptop or CPU, thorough research is vital and the following factors are invloved:

Reviews and expert opinions can help you make an informed decision on best laptop processor. Websites like Tom’s Hardware, Notebookcheck, and AnandTech provide detailed CPU reviews and performance comparisons. User reviews on platforms like Amazon and Best Buy can also offer valuable insights.
Additional Considerations When Choosing a Laptop CPU
Thermal Management and Cooling Solutions
One critical aspect of CPU performance, especially in laptops, is thermal management. Laptops, unlike desktop PCs, have limited space for cooling solutions. Therefore, CPU performance can be constrained by heat build-up. So, even if you have a more powerful CPU but it doesn’t have good thermals, it could cause issues.
As the CPU works harder, it generates more heat, which can cause thermal throttling (when the processor slows down to avoid overheating).

Manufacturers often use various cooling techniques to mitigate this issue, including heat pipes, fans, and thermal paste. Some premium laptops, particularly gaming laptops, come with advanced cooling solutions, such as vapor chambers and liquid cooling systems, to maintain high performance during intensive tasks.
It’s important to choose a laptop that matches your thermal requirements, particularly for tasks like gaming or content creation, which push the machine and CPU to its limits.
Impact of Clock Speed and Turbo Boost
While the core count is essential to overall performance, clock speed and turbo boost are also key performance factors. The clock speed, measured in gigahertz (GHz), represents how quickly a CPU can process instructions. CPUs with higher base clock speeds can execute tasks faster. However, clock speed is not the sole determinant of performance.
Many modern CPUs come with turbo boost technology, which allows the processor to temporarily increase its clock speed when necessary for demanding tasks. For instance, Intel’s Turbo Boost or AMD’s Precision Boost adjusts the clock speed based on thermal conditions and workload.
This feature can provide your laptop processor a significant performance boost in short bursts, allowing the CPU to perform better during heavy multitasking, gaming, or video editing. If your work often involves CPU-intensive tasks, choosing a laptop processor with a higher turbo boost potential can be a smart decision.
CPU Generations and Improvements
Both Intel and AMD regularly release new generations of CPUs, with each iteration offering incremental improvements in performance, efficiency, and features.
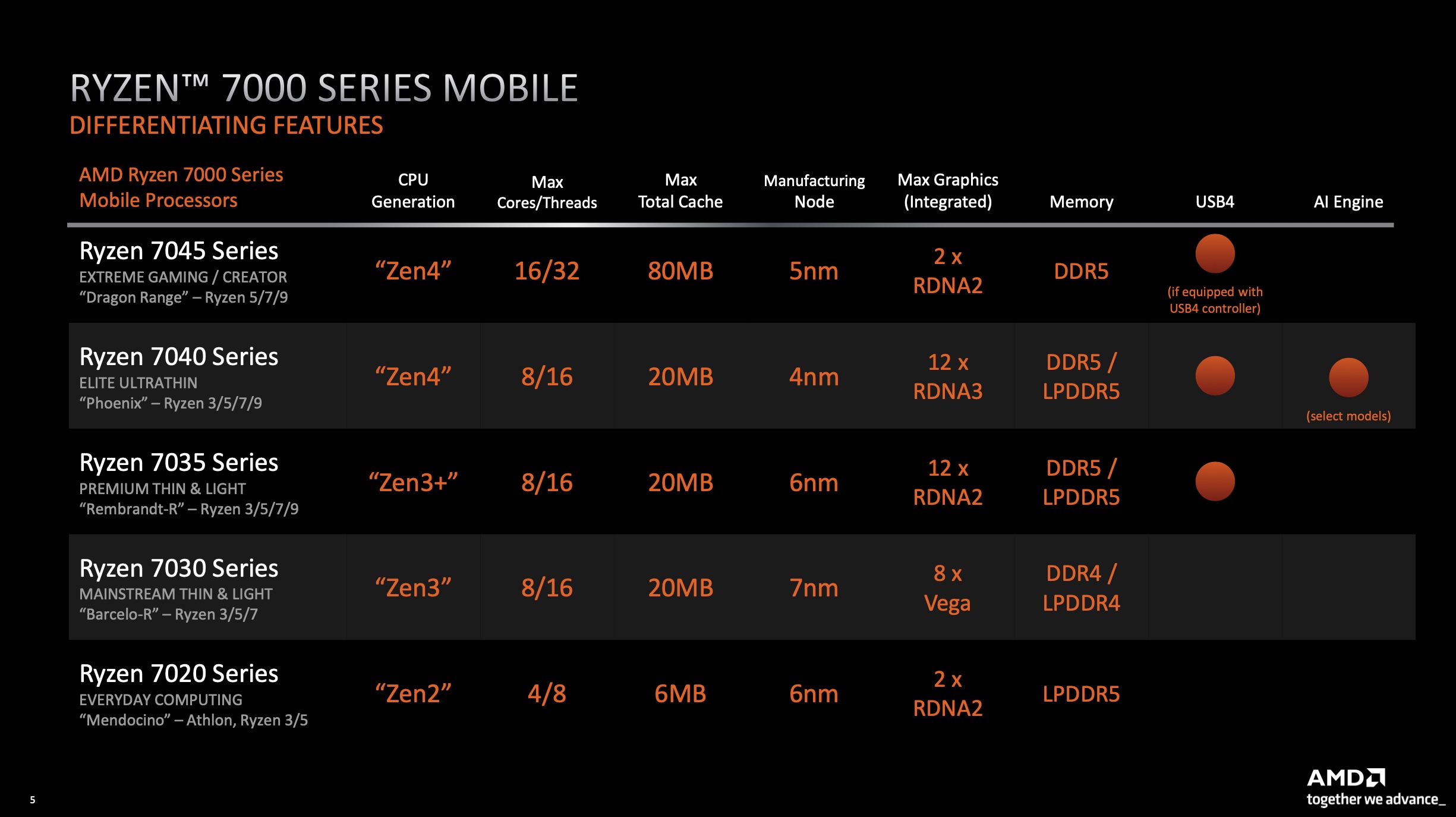
For example, Intel’s 11th generation Core processors introduced substantial improvements in integrated graphics and AI-based performance, while AMD’s Ryzen 5000 series brought considerable gains in single-core and multi-core performance.
When purchasing a laptop, be sure to check the generation of the CPU. A newer generation generally means better performance and power efficiency, but the performance leap may not be dramatic in all cases.
It’s crucial to look at the specific gains made by each new generation intel processor, as it has factors that could impact your decision if you are balancing budget with performance.
The Role of Hyper-Threading and SMT
In addition to core count, CPU technologies like Intel’s Hyper-Threading (HT) and AMD’s Simultaneous Multi-Threading (SMT) enhance performance by allowing each physical core to handle two threads instead of one. This increases multitasking and overall processing efficiency, particularly in applications that benefit from parallel processing.
For demanding tasks like video editing, 3D rendering, or running virtual machines, a CPU with Hyper-Threading or SMT can dramatically boost productivity. If you expect your machine to handle multiple applications simultaneously or work with demanding software, opting for a processor that supports these technologies is beneficial.
Considering Other Laptop Features Alongside the CPU
While the CPU is a vital component, it’s important to remember that other features contribute significantly to overall laptop performance. These include:
1. RAM and Storage:
For optimal performance, ensure that your laptop includes at least 256GB or 512GB of SSD storage, especially if you work with large files.
2. Display:
3. Battery Life:
The CPU plays a vital role in determining battery life. Energy-efficient processors, such as Intel’s U-series or AMD’s Ryzen 6000 series, are designed to provide good performance without draining the battery too quickly.
If you’re planning to use your laptop on the go, it’s essential to balance your choice of CPU with a battery that can last for the duration of your workday. Look for laptops with larger battery capacities, especially if you plan to use demanding applications.

4. Build Quality and Portability:
For users who require portability, such as frequent travelers, lightweight and slim laptops are crucial. These laptops usually prioritize low-power CPUs to extend battery life. However, high-performance CPUs are available in thinner designs with innovative cooling systems, which can still provide great power without sacrificing portability.
Always consider the overall build quality and portability of the new laptop first, particularly if you need to carry it for extended periods.
Choosing the very best laptop processor and the best CPU also requires balancing performance, power consumption, and budget. Here are the key takeaways:
Whether you’re a casual user, gamer, or professional, there’s the best processor and a perfect CPU out there for you.
When it comes to buying a laptop, the CPU (Central Processing Unit) is one of the most critical components to consider.
This guide will help you understand laptop CPUs and how to choose the best one for your needs.
A laptop CPU (Central Processing Unit) is the brain of a laptop, responsible for executing instructions and managing various tasks together. Whether you’re opening an application, streaming a video, or playing a game, the CPU is working behind the scenes to do simple tasks and ensure smooth operation.

Laptop CPUs are designed to balance processing power, speed, energy efficiency, and heat generation. Unlike desktop CPUs, which prioritize raw power, laptop CPUs focus on delivering adequate performance while maintaining a compact and energy-efficient design.
Understanding core count, processing power, CPU cost, and architecture is vital when evaluating CPU performance:
The two dominant players in the laptop CPU market are Intel and AMD:
Ryzen processors also typically feature more cores and threads, making them excellent for multitasking and productivity.

Both brands cater to a wide range of users from casual laptop users to professionals and gamers.
Laptop CPUs can be categorized into three performance tiers:
The choice between integrated and dedicated graphics depends on your usage:

For users focusing on general productivity, integrated graphics are usually sufficient. Gamers and creators should opt for dedicated GPUs paired with high-end CPUs.
Selecting the right CPU starts with understanding your usage patterns:

Balancing performance and power consumption is crucial for laptops:
To maximize battery life without sacrificing performance, consider CPUs designed for efficiency, like Intel’s EVO-certified processors or AMD’s Ryzen 6000 series processor.
When choosing a new laptop or CPU, thorough research is vital and the following factors are invloved:

Reviews and expert opinions can help you make an informed decision on best laptop processor. Websites like Tom’s Hardware, Notebookcheck, and AnandTech provide detailed CPU reviews and performance comparisons. User reviews on platforms like Amazon and Best Buy can also offer valuable insights.
Additional Considerations When Choosing a Laptop CPU
Thermal Management and Cooling Solutions
One critical aspect of CPU performance, especially in laptops, is thermal management. Laptops, unlike desktop PCs, have limited space for cooling solutions. Therefore, CPU performance can be constrained by heat build-up. So, even if you have a more powerful CPU but it doesn’t have good thermals, it could cause issues.
As the CPU works harder, it generates more heat, which can cause thermal throttling (when the processor slows down to avoid overheating).

Manufacturers often use various cooling techniques to mitigate this issue, including heat pipes, fans, and thermal paste. Some premium laptops, particularly gaming laptops, come with advanced cooling solutions, such as vapor chambers and liquid cooling systems, to maintain high performance during intensive tasks.
It’s important to choose a laptop that matches your thermal requirements, particularly for tasks like gaming or content creation, which push the machine and CPU to its limits.
Impact of Clock Speed and Turbo Boost
While the core count is essential to overall performance, clock speed and turbo boost are also key performance factors. The clock speed, measured in gigahertz (GHz), represents how quickly a CPU can process instructions. CPUs with higher base clock speeds can execute tasks faster. However, clock speed is not the sole determinant of performance.
Many modern CPUs come with turbo boost technology, which allows the processor to temporarily increase its clock speed when necessary for demanding tasks. For instance, Intel’s Turbo Boost or AMD’s Precision Boost adjusts the clock speed based on thermal conditions and workload.
This feature can provide your laptop processor a significant performance boost in short bursts, allowing the CPU to perform better during heavy multitasking, gaming, or video editing. If your work often involves CPU-intensive tasks, choosing a laptop processor with a higher turbo boost potential can be a smart decision.
CPU Generations and Improvements
Both Intel and AMD regularly release new generations of CPUs, with each iteration offering incremental improvements in performance, efficiency, and features.

For example, Intel’s 11th generation Core processors introduced substantial improvements in integrated graphics and AI-based performance, while AMD’s Ryzen 5000 series brought considerable gains in single-core and multi-core performance.
When purchasing a laptop, be sure to check the generation of the CPU. A newer generation generally means better performance and power efficiency, but the performance leap may not be dramatic in all cases.
It’s crucial to look at the specific gains made by each new generation intel processor, as it has factors that could impact your decision if you are balancing budget with performance.
The Role of Hyper-Threading and SMT
In addition to core count, CPU technologies like Intel’s Hyper-Threading (HT) and AMD’s Simultaneous Multi-Threading (SMT) enhance performance by allowing each physical core to handle two threads instead of one. This increases multitasking and overall processing efficiency, particularly in applications that benefit from parallel processing.
For demanding tasks like video editing, 3D rendering, or running virtual machines, a CPU with Hyper-Threading or SMT can dramatically boost productivity. If you expect your machine to handle multiple applications simultaneously or work with demanding software, opting for a processor that supports these technologies is beneficial.
Considering Other Laptop Features Alongside the CPU
While the CPU is a vital component, it’s important to remember that other features contribute significantly to overall laptop performance. These include:
1. RAM and Storage:
For optimal performance, ensure that your laptop includes at least 256GB or 512GB of SSD storage, especially if you work with large files.
2. Display:
3. Battery Life:
The CPU plays a vital role in determining battery life. Energy-efficient processors, such as Intel’s U-series or AMD’s Ryzen 6000 series, are designed to provide good performance without draining the battery too quickly.
If you’re planning to use your laptop on the go, it’s essential to balance your choice of CPU with a battery that can last for the duration of your workday. Look for laptops with larger battery capacities, especially if you plan to use demanding applications.

4. Build Quality and Portability:
For users who require portability, such as frequent travelers, lightweight and slim laptops are crucial. These laptops usually prioritize low-power CPUs to extend battery life. However, high-performance CPUs are available in thinner designs with innovative cooling systems, which can still provide great power without sacrificing portability.
Always consider the overall build quality and portability of the new laptop first, particularly if you need to carry it for extended periods.
Choosing the very best laptop processor and the best CPU also requires balancing performance, power consumption, and budget. Here are the key takeaways:
Whether you’re a casual user, gamer, or professional, there’s the best processor and a perfect CPU out there for you.

Indie climbing game Cairn has quickly become one of 2026’s biggest early hits, reaching more than 300,000 players shortly after

HumanitZ, a new co-op zombie survival game by Yodubzz Studios, has officially launched its version 1.0 on Steam after two

New leaks surrounding WWE 2K26 have caught the attention of WWE fans, hinting at the return of controversial features from